 |
|
Tham luận, báo cáo và bài viết khoa học tại hội nghị, tạp chí y khoa quốc tế

1. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ LẦN THỨ 53 (AASLD Boston 1 - 5/11/2002)
CLINICAL RESEARCH ON THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS B WITH THYMOSIN- a1 AND LAMIVUDINE VERSUS INTERFERON-α AND LAMIVUDINE
Dr. Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Head of Hepatology Dep. –Medical Medic Center-HCM City
Thymosin-α1 with lamivudine may be more effective than IFN-α with lamivudine .Compared with IFN-a and Lamivudine , Thymosin a1 and Lamivudine are better tolerated and seem to induce a gradual and more sustained ALT normalization and HBVDNA loss .However such results need to be confirmed with a randomized double blind study with larger number of patients in the future.
Abstract 1843- Hepatology Vol 36 N 4
2. HỘI NGHỊ TIÊU HÓA THẾ GIỚI ( WCOG) Bangkok – Thailand - 24/2 - 1/3/2002
Poster :
Dr.Pham Thi Thu Thuy
MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER
The association of diabetes mellitus with chronic liver disease, particularly cirrhosis, was recognized many years ago. Preliminary studies suggest that hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection may be an additional risk factor for the development of diabetes mellitus .To further study the correlation of HCV infection and diabetes, we performed a retrospective analysis of 7234 patients with vial hepatitis and analyzed whether age,sex, hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, HCV infection, and cirrhosis were independently association with diabetes. Second a case-control study was conducted to determine the seroprevalence of HCV infection in a cohort of 641 diabetic patients . Diabetes was observed in 11.51% of HCV –infected patients compared with 5.18% of HBV –infected patients .The older the age is the higher the prevalence of diabetes mellitus is . In the diabetes cohort , 36.36% were found to be infected with HCV compared with 4% of control patients. HCV serotype 2 was observed in 36.36% of HCV-RNA -positive diabetic patients vesus 10.52% of HCV-infected control . In conclusion ,the data suggest a relatively strong association between HCV infection diabetes, because diabetes have an increased frequency of HCV infection , particularly with serotype 2 .Furthermore , it is possible that HCV infection may serve as an additional risk factor for development of diabetes, beyond that , attributes chronic liver disease alone.

3. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á –THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG (APASL) Bali - Indonesia- 18 - 21/8/2005
Poster 327
Prevalence of HCV genotypes in Vietnam
Thu Thuy -Tan Dat- Thanh Tong- BaoToan - Ba Tong- Oanh- Trang
MEDIC Medical Centre, HCM City, Viet Nam
Background:
HCV genotypes are distributed differently depending on geography and etiology of infection. We studied the spectrum of HCV genotypes in chronic liver Vietnamese patients. The incidence of Hepatitis C (HCV) isolates found in clinical practice is of great clinical significance to the treatment of HCV infected patients as different subtypes may respond unequally to therapy. Beside, both viral load and HCV genotype may have relevance in chronically infected
Objectives: To evaluate the prevalence of HCV genotypes in Vietnamese patients.
Comparison of serum virus loads among Patients infected with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) genotypes 1, 2 and 6
Methods: A total of 202 HCV RNA positive patients with chronic hepatitis were enrolled (Male 59,4%, female 40,6% with mean age of patients 47,89 ± 10,87 years
) from April 2004 to Nov 2004. At the same time, we collected 149 random serums in this group to perform Branched DNA for quantitative HCVRNA.
All samples were amplified RT – PCR (In-house PCR amplification with NP & OP primer from Bayer Corporation) in the 5’ UT region. Biotinylated amplicon, generated by PCR of HCVRNA is hybridized to immobilized probes. The probes, which are bound to a nitrocellulose strip by a poly (T) tail, are specific for the 5’ UT of the different HCV genotypes (The versant HCV Genotype Assay, Bayer).
Statistical analysis: SPSS for Window 7.5 software. The data were expressed as percent, mean±SD. Chi-square test was used to analyze the discontinuous variables.
Results:
Genotypes 1 and 6 were the commonest genotypes, followed by type 2 and the rare genotype 3 in alone patient. Genotype 1 was seen in 58,9% (Type 1: 6,9%; 1a: 6,9%; 1a/1b: 0,5%; 1b: 44,6%) while genotype 6a in 25,2%, genotype 2 in 11,4% (type 2: 2%; type 2a/2c: 9,4%) and genotype 3b was 0,5%, eight samples (4%) were unclassified. Then we performed sequencing based on 5’UT with Trugene system identified genotype 1 (1 case), 1b (2 cases), 6a (5 cases) but not typed by LiPA. 149 patients had viral loads above 3200 copies/ml (Range: 4000 - > 40,000,000 copies/ml, with 5,18x106 ±
6.53x106 copies/ml.
). HCV genotype 1, 2, 6 had quantity HCV RNA above 2x106 copies/ml was 55, 10, 23 cases, and below 2x106 copies/ml was 32, 9, 20 cases, respectively. We observed no significant difference in virus load between patients infected with genotype 1, 2, 6.(P>0,05)
Conclusions:
Our study indicated that HCV genotypes 1 and 6 are common in Viet Nam. With subtype 1b is the most common. A unique genotype 3b was detected in our patients. There isn’t relationship between HCV genotype and viremia levels. The TruGene system, a direct sequencing method, is more efficient in the identification of HCV genotype.
Liver International Hepatology 2005- Abstract book

4. HỘI NGHỊ TIÊU HÓA THẾ GIỚI (WCOG) Montreal – Canada - 12 - 14/9/2005
President poster: PP7
Clinical research on the treatment of chronic hepatitis B with thymosin- a1 and lamivudine versus interferon-α and lamivudine
Pham Thi Thu Thuy - Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center-HCM City
It has recently been shown that thymisin-a 1, a synthetic polypeptide of thymic origin, an immune modifier, is able to promote disease remission and inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication. We evaluated the efficacy and safety of thymosin- a1 and lamivudine treatment compared with interferon -a and lamivudine treatment on the patients with chronic hepatitis B who were difficult to be treated well, failed to lamivudine treatment alone. Eighty three patients (Age: 18-60) with confirmed chronic hepatitis B and positive for HBV DNA with an elevated ALT of at least two times normal who failed to lamivudine treatment alone were entered into this study. Eighty three patients were randomly assigned to receive either thymosin- a1 1.6mg SC twice weekly and lamivudine 100mg p.o daily or 5MU of interferon-a three times weekly and lamivudine 100mg p.o daily for 6 months. At the end of treatment, complete response (defined as ALT normalization and HBVDNA loss) occurred in 11 of 43 (25.58%) in group I and in 22 of 40( 55%) in group II (p<0.01) . After a follow up period of 6 months, a complete response was observed in 18 of 43 (41.86%) in group I and 19 of 40 (47.50%) in group II (p>0.05) . After a follow up period of 12 months, a complete response was observed in 25 of 43 (58.14 %) in group I and 12 of 40 (30%) in group II (p<0.05) . So thymosin- a1 with lamivudine may be more effective than interferon-a and lamivudine by immunomodulatory effect. Compared with interferon-a and lamivudine, thymosin- a1 and lamivudine are better tolerated and seem to induce a gradual and more sustained ALT normalization and HBVDNA loss. Unlike interferon-a , thymosin- a1 was well tolerated by all patients. The side effect of thymosin- a1 group was rare .The better response was in HbeAg-negative and HBVDNA- positive patients. However such results need to be confirmed with a randomized double blind study with larger number of patients in the future.

5. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT THẾ GIỚI Cairo- Ai Cập – 7—11/9/2006
Poster 114
Applying Sequencing To Identify Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes And Mutations
Ho Tan Dat, Pham Thi Thu Thuy,
Nguyen Bao Toan, Nguyen Thanh Tong
MEDIC Medical Center –Ho Chi Minh City-VietNam
Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) can be classified into 8 genotypes A through H based on an intergroup divergence of 8% or more in the complete nucleotide sequence, and the different distribution of various genotypes in different continents, countries. The identification of HBV genotypes are more concerned as it is HBV genotypes relating to clinical manifestation, activity of liver disease as well as treatment responses of Hepatitis B. Additionally, the discovery of resistance to medicines in HBV treatment plays a very important role from which we can have an appropriate and effective choice in Hepatitis B treatment. We have applied the Sequencing by TruGene (Bayer) to identify Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes and Mutations. From August 2004 to November 2005, in MEDIC laboratory, we have implemented sequencing for 69 cases Vietnamese with Chronic Hepatitis B on Lamivudine treatment in which: 55 cases are males (take 79.7%) and 14 cases are females (take 20.3%), medium age: 34.6±10.3. All cases are HBVDNA (+) in which: 50 cases are HbeAg (+) (72.5%) and 19 cases are HbeAg(-) (27.5%). There are only two genotypes of HBV: genotype B and genotype C, in which 45 cases are genotypes B (65.2%) and 24 cases are genotype C (34.8%).
Totally there are 41 cases (59.4%) mutations with following established proportion and types: L180M (5.8%); L180M & M204I (8.7%); L180M & M204V (30.4%); L180M, M204V & V207I (1.4%); M204I (8.7%); M204I&V207I (1.4%); M204V (2.9%).
There are 25 cases mutations in 45 cases of genotypes B (55.6%) and 16 cases in 24 cases of genotypes C (66.7%). All patients are on Lamivudine treatment with average time is 2.4±0.9 years, the corresponding number of patients in treatment period of 1,2,3,4 year are 10, 29, 21, 9. The proportion of developing mutations after 1, 2, 3, 4 years of treatment with Lamivudine is 20%; 55.2%; 76.2%; 77.8%.
We have found that – with above preliminary results – the sequencing plays a very important role in identifying Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes and Mutations. From those results we can approach an optimal treatment course.
Liver International Vol 26-Supp 1
.jpg)

6. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á- THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG (APASL) Kyoto - Japan - 26 - 30/3/2007
Poster 0411: được giải Best Poster
COMPARISON BETWEEN THE TWO PEGINTERFERONS ALFA IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS C
Dr.Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Dr.Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center-HCM City
In order to have the evaluation of efficacy, safety and to detect the predictors for sustained viral response of two Peginterferons, we have implemented a matched pair study on treatment naïve chronic hepatitis C patients treated with weight –based Peginterferon alfa -2b or fixed dose Peginterferon alfa- 2a plus Ribavirin.
There are 211 naïve chronic hepatitis C patients aged from 18 to 68, divided into two equal groups in clinical manifestations. Group I ( N=116; 67 genotype 1, 15 genotype 2, 34 genotype 6) were treated with Peg-IFN alfa-2b, 1.5mcg/kg qweek plus Ribavirin 15mg/kg/day; Group II ( N=95; 56 genotype 1, 11 genotype 2, 28 genotype 6) were treated with peg-IFN alfa-2a 180mcg/week plus Ribavirin 15mg/kg/ day. The time of treatment was 48 weeks. Sustained viral response was undetectable HCVRNA after 24 weeks of follow-up. The treatment outcome can be predicted by analyzing various data on age, sex, weight, serum ALT, genotype and virus load. The sustained viral response rate of Group I was not different from of GroupII on total patients ( 62.06% vs. 61.05%, p>0.05) . The relapse in two groups were also similar (19.10% vs. 19.44%, p>0.05). The sustained viral response with treatment of Peg-IFN alfa-2b was better than with Peg-IFN alfa- 2a in group of high-weighed patients ( 28.57% vs. 61.9%, p<0.01). Baseline ALT, age, sex, genotype, virus load were not statistically significant predictors of sustained viral response between two Peginterferons .
In conclusion, the sustained viral response rate is similar in naïve chronic hepatitis C patients treated with Peg-IFN alfa-2a or Peg-IFN alfa-2b.Peg-IFN alfa-2b seems to be better in high-weighed patients. Side effect of thrombocytopenia more frequently occurs in treatment with Peg-IFN alfa-2a, however it should be further studied in future.
International Hepatology 2007-Vol1-N1
.jpg)


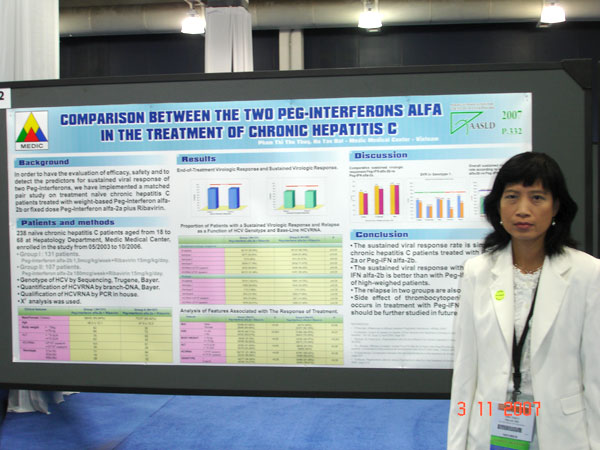
7. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ LẦN THỨ 58 (AASLD) Boston 2 - 6/11/2007
Poster 332
COMPARISON BETWEEN THE TWO PEGINTERFERONS ALFA IN THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC HEPATITIS C
Dr.Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Dr.Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center-HCM City
Abstract 332, Hepatology Vol 46, N 4
8. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á –THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG (APASL) Hongkong 13 - 17/2/2009
Presentation: FP 053
PEGYLATED INTERFERON ALFA-2a PLUS RIBAVIRIN IN CHRONIC HEPATITIS C PATIENTS WITH GENOTYPE 6
DR. Pham Thi Thu Thuy
DR. Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center- HCM City-VN
Aims: The effectiveness of the combined treatment Peginterferon alfa -2a and ribavirin in Hepatitis C were intensively studied, but mainly for genotype 1. Little information was known about the treatment of genotype 6 which occurred at high frequency in several Asian countries, including China, Viet Nam, Hongkong and Thailand etc. The aims of the study therefore are to evaluate the effectiveness, safety and other influential factors at the therapeutic regime of Peginterferon alfa -2a combined with Ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 6 in Vietnam.
Patients and methods: 75 chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 6 were classified into two groups. Group I included 42 naïve patients, group II included 33 patients who had previously failed with standard Interferon –alfa. All the patients were treated with Peginterferon alfa-2a 180mcg/w combined with Ribavirin 15mg/kg/day; the period of treatment time was 48 weeks. Sustained viral response was defined as undetectable HCVRNA after 24 weeks of follow-up. Ages, sexes, increase of ALT, AST/ALT ratio and viral load were the factors for evaluating the effectiveness of the treatment and the prognosis.
Results: Sustained virus responses were nearly the same between the two groups (Group I: 69.04%; Group II: 60.60%; p>0.05). Normal transaminase levels at week 72 were 73.80%, 63.63% in group I and group II, respectively. It was found that younger patients , AST/ALT ratio lower than 1 were the factors that could induce a higher sustained viral response in every group. Viral load only affected to sustained viral response in patients were previous treatment failed . Patients who had rapid viral responses, almost all had sustained viral responses.
Conclusion: Patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 who have never been treated or have failed with standard interferon showed good responses when treated by Peginterferon alfa-2a combined with Ribavirin . The sustained viral response was better than that of genotype 1. Patients especially had rapid viral responses; almost all had sustained viral responses. So will the treatment time be shorten for these patients? We will need further studies in future.
International Hepatology- 2009- Vol 3-N 1

Poster E058
ENTECAVIR FOR TREATMENT OF LAMIVUDINE –REFRACTORY PATIENTS CHRONIC HEPATITIS B
Dr.PHAM THI THU THUY
Dr.HO TAN DAT
MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER-HCM CITY
Lamivudine treatment is associated with frequent development of resistant hepatitis B virus. This incidence especially is higher in the longer time of treatment and loss of treatment benefit. Entercavir is a new antiviral agent shown its high efficacy even in cases of mutations with Lamivudine resistance. In this study, we would like to evaluate the efficacy, the safety of Entercavir in treatment of Lamivudine-refractory patients chronic hepatitis B. To analyze factors that influent to the efficacy of treatment.
Sixty chronic hepatitis B patients with evidence of Lamivudine resistance were randomly divided into two groups in proportion of 3:1. Group I (n=45) used Entecavir 1mg/day, group II (n=15) used Lamivudine 100mg/day. Treatment time was 48 weeks. All data were evaluated in the end of the treatment: histology, ALT, HBVDNA. The factors such as: age, sex, ALT, HBVDNA, genotype, HBeAg were analyzed to evaluate their influences to the treatment.
The results have showed HBVDNA<2000 copies/mL in Entecavir group 37.78% vs. 0% Lamivudine group (p<0.01). HBVDNA negative in Entecavir group was 17.77% and incidence of seroconversion of HBeAg was 8.82%. ALT was normal in Entecavir group 77.77% vs. 26.66% in Lamivudine group (p<0.001).Histologic improvement in Entecavir group was 37.77% vs.6.66% in Lamivudine group (p<0.05). Patients with HBeAg negative, genotype B, low virus load were shown better results.
Entecavir was shown to be efficacious in the treatment for chronic hepatitis B patients experienced with Lamivudine resistance. Entercavir is safe, with almost no side effects. Factors such as HBeAg negative, genotype B, low virus load seems to be better in response to the treatment. The recurrence or mutation of Entecavir resistance should be studied further in future.
International Hepatology- 2009- Vol 3-N 1

9. HỘI NGHỊ TIÊU HÓA HOA KY (DDW) Chicago 29/5 - 5/6/2009
Poster M 1795
PEGYLATED INTERFERON ALFA-2a PLUS RIBAVIRIN IN CHRONIC HEPATITIS C PATIENTS WITH GENOTYPE 6
DR. Pham Thi Thu Thuy
DR. Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center- HCM City-VN

10. HỘI NGHỊ TIÊU HÓA THẾ GIỚI (WCOG) London 21 - 28/11/2009
Poster 1978
PEG-INTERFERON ALFA-2a AND RIBAVIRIN IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC HEPATITIS C WHO HAVE FAILED PRIOR TREATMENT
Dr.Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Dr.Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center
Summary:
Aims: Chronic hepatitis C patients who were treated with Interferon alfa afterward having a failure of therapy or relapse are not very few. So, a question that if these cases could be retreated with Peginterferon-alfa? The aims of the study are to evaluate the effectiveness, safety and other influenced factors to the therapeutic regime of Peginterferon alfa-2a combined with Ribavirin.
Patients and Methods: 117 chronic hepatitis C patients were classified into two groups. Group I consisted of 63 patients who were previously failed with interferon –alfa, of those including HCV genotype 1 (n=41), genotype 2 (n=7) and genotype 6 (n=15). Group II included 54 patients who had a relapse after stopping treatment, involving HCV genotype 1 (n=40), genotype 2 (n=5) and genotype 6 (n=9). All the patients were retreated with Peginterferon alfa-2a 180mcg/week combined with Ribavirin 15mg/kg/day, period of treatment time were 48 weeks. Sustained viral response was defined as undetectable HCVRNA after 24 weeks of follow-up. Ages, sex, AST/ALT ratio, HCV genotype, viral load, previously treated with interferon alone or combined with Ribavirin were the factors for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment and prognosis.
Results: The results were found that: Sustained viral response was significantly higher in the relapsed group than that in the non-respond group (44.44 % vs. 26.98 %, p<0.05), in particular in patients with genotype 1. The rate of relapse in non-respond group was also higher than that in the relapsed group. We found that younger patients, without HCV genotype 1, AST/ALT ratio lower than 1, previously treated with interferon alone were the factors that could induce a higher sustained viral response in every group. Viral load only affected to sustained viral response in non-respond group. Dose reduction of Peginterferon or Ribavirin do not cause any influences on sustained viral response.
Conclusions: In chronic hepatitis C patients with difficulties of treatment, non-response or relapsed with previous therapy of interferon alfa still being able to gain a sustained viral response when retreated with Peginterferon alfa-2a plus Ribavirin. Relapsed patients or previously treated with interferon alone could have a successful potential of retreatment. Dose reduction of Peginterferon or Ribavirin does not cause any influences on sustained viral response.
An International of journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology – November 2009- Vol 58- Supp II

11. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á-THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG
BẮC KINH –TRUNG QUỐC- 24/3-----28/03/2010
Preaentation : FP 100
AN OPTIMAL DURATION OF TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC HEPATITIS C GENOTYPE 1 PATIENTS
Dr. Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Dr. Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center-HCM City
Summary:
Aims: Combination of peginterferon with ribavirin in treatment for chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 in 48 weeks was shown to have rather high relapse rate. There are different opinions on treatment course, it’s considered that longer treatment course being better outcomes. The aims of the study therefore are to compare the effectiveness between the standard course of treatment (48 weeks) and prolong course (72 weeks). We will consider which factors leading to predict the sustained virologic response.
Patients and methods: 108 hepatitis C patients with genotype 1 were classified into two groups. Group I included 63 patients who received 48 weeks of treatment. Group II included 45 patients received 72 weeks of treatment. All the patients were treated with Peginterferon alfa-2a 180mcg/week combined with Ribavirin 15 mcg/kg/day. Ages, sex, increase of ALT, rate of rapid virological response, viral load were the factors for evaluating the effectiveness of the treatment and the prognosis.
Results: sustained virological response in group II were higher than in Group I (84.44% vs. 55.55%, p<0.01). Patients in group II who became negative for HCVRNA between weeks 12 and 24 had significantly higher SVR rate than that of group I (54.54% vs. 6.66%, p<0.001). Factors associated with an SVR include younger age, an AST/ALT ratio lower than 1, FibroScan from F1 to F3 and lower viral load in group I. In group II, oly age impact on SVR. SVR rates were highest in those patients which achieved an RVR.
Conclusion: Patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 who were treated by peginterferon alfa combined with Ribavirin in 72 weeks extended treatment shown higher sustained viral response than those in 48 weeks. RVR was a very strong predictor of SVR. The patients with late viral negativity for HCVRNA should be treated for 72 weeks. No serious adverse events or withdrawals for safety reasons were seen in both treatment regimens.
Hepatology International 2010 –Vol 40 –N1-FP 100
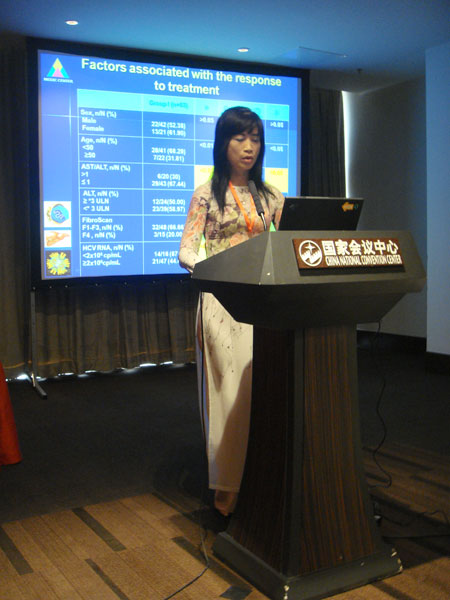

12. HỘI NGHỊ CHUYÊN SÂU NGHIÊN CỨU VIÊM GAN CHÂU Á- THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG LẦN THỨ I - APPH 2011- TP HCM- 18-19/06/2011
An optimal duration of treatment for chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 patients
Dr. PHAM THI THU THUY
Dr. HO TAN DAT
MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER-HCM CITY
Optimal duration of the combined treatment of peginterferon alfa-2a and ribavirin (Peg-IFN/RBV) in chronic hepatitis C has been intensively studied for genotypes 1, 2 and 3. In contrast little information is known about the optimal duration of therapy for patients with HCV genotype 6. At present, guidelines state that Asian G6 patients should undergo 48 weeks’ treatment with Peg-IFN/RBV;1 however, more recent data suggest that 24 weeks’ treatment may be as effective,2,3 hence there is a need for further studies to confirm optimal treatment duration in this population.
During this presentation one such study will be discussed. The aim of the study was to compare efficacy between a standard course of treatment of 48 weeks (group 1) and a shorter duration of treatment of 24 weeks (group 2). Baseline and on-treatment factors were also assessed for their effect on SVR. SVR results were similar between the two groups (79.36% in group 1 versus 72.41% in group 2, p>0.05) suggesting that efficacy is not compromised by a shortened treatment duration. Patients who were younger in age and had an AST/ALT ratio lower than 1 were found to achieve higher SVR rates in both treatment groups. Degree of fibrosis and viral load only affected SVR in patients who received the shortened treatment duration of 24 weeks. Achieving an RVR was highly indicative of achieving an SVR especially in patients treated for 24 weeks.
In conclusion, patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 6 treated with Peg-IFN/RBV for 24 weeks versus 48 weeks achieved similar SVR rates. RVR was a very strong predictor of SVR regardless of treatment duration however patients that did not achieve RVR should be treated for 48 weeks.
1. Antaki N, et al. Liver Int 2010; 30: 342
2. Lam KD, et al. Hepatology 2010; 52: 1573
3. Zhou YQ, et al. J Viral Hepat 2010; Epub ahead of print


13.HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ- AASLD- SAN FRANCISCO- 4/11—8/11/2011
Poster 958
AN OPTIMAL DURATION OF TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC HEPATITIS C GENOTYPE 6 PATIENTS
Dr. Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Dr. Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center- Ho Chi Minh City- Viet Nam


Hepatology –V 54, N 4 (Suppl) October 2011- Abstract 958
14. HÔI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á-THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG 16/-2- 19/02/2012
Poster PP12-027
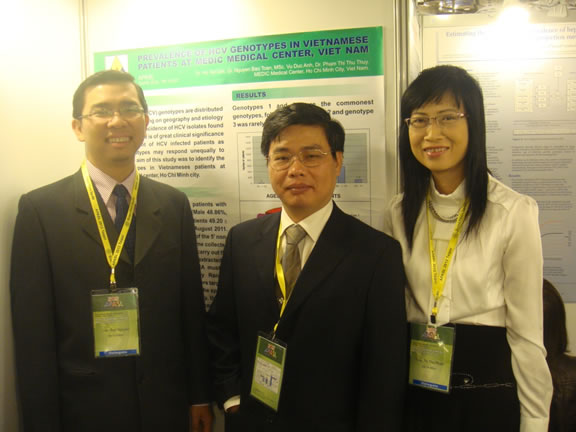
PREVALENCE OF HCV GENOTYPES IN VIETNAMESE PATIENTS AT MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER, VIET NAM
Dr. Ho Tan Dat, Dr. Nguyen Bao Toan, Dr. Vu Duc Anh, Dr. Pham Thi Thu Thuy.
MEDIC Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam.
Background:
Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) genotypes are distributed differently depending on geography and etiology of infection. The incidence of HCV isolates found in clinical practice is of great clinical significance to the treatment of HCV infected patients. The aim of this study was to identify the HCV genotypes in Vietnamese patients at MEDIC medical center, Ho Chi Minh City.
Methods:
A total of 3686 HCVRNA positive patients with chronic hepatitis C were enrolled (Male 48.86%, female 51.14% with mean age of patients 49.20 ± 11.48 years) from January 2007 to August 2011.
We have performed the sequencing of the 5' non-coding of the hepatitis C virus genome collected from sera with HCVRNA positive. To carry out the sequencing, first the sera must be extracted to collect the total RNA, and then the RNA must be reverse transcripted into cDNA by Random primers. The PCR using specific primers targeted the 5' non-coding region will amplify the specific fragment 244bp from the cDNA. Finally, the PCR product will enter the sequencing process using the Trugene sequencer of Siemens.
Results:
Genotypes 1 and 6 were the commonest genotypes, followed by genotype 2 and genotype 3 was rarely found.
Genotype 1 was seen in 59.98% (Type 1: 9.39%; type 1a: 12.96%; type 1b: 37.63%) while genotype 6 in 24.15% (Type 6: 1.28%, type 6a: 22.68%, type 6b: 0.19%), genotype 2 in 15.82% (Type 2: 0.3%%; type 2a: 13.67%, type 2b: 0.52%, type 2c: 1.19%, type 2d: 0.14%) and genotype 3 was 0.05% ( Type 3a: 0.025%; type 3b: 0.025%).
Conclusions:
Our study indicated that HCV genotypes 1 and 6 are common in Vietnamese patients. Subtype 1b is the most common one. Only 0.05% of patients carried genotype 3.

Hepatology International, V 6,N1, 2012, Abstract pp12-027
16. Hội nghị gan mật toàn quốc tại Đà nẳng 17-18/08/2012
Xem nội dung báo cáo (file pdf)

17. Hội nghị gan mật TP. Hồ Chí Minh 25/11/2012
Xem nội dung báo cáo (pdf file)


18. Hội nghị: Chung tay vì một Việt nam không viêm gan.
TP. Hồ Chí Minh 13 - 03 - 2013
Hà nội 15 - 03 - 2013
Xem nội dung báo cáo (file pdf)



19. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á- THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG - SINGAPORE 6/06 - 10/06/2013
POSTER 365
Impact of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of IL28B on SVR in Treatment Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 6 in Vietnamese Patients
Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center - Ho Chi Minh City-Viet Nam
Aims:
-To determine the relationship between IL28B single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and sustained virologic response (SVR) rates to combination therapy of Peginterferon alfa and Ribavirin.
- Comparing SNPs allele frequencies in relation to other factors such as age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan.
Method:
The study is designed as a retrospective review of the medical records of chronic HCV patients with genotype 6 . SNP of IL28B (rs12979860) was identified by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of samples from 89 patients who were treated with Peginterferon alfa and Ribavirin . The duration of treatment was 48 weeks.
Results:
Patients with CC had higher rates of rapid virologic response (RVR) (84.44% vs. 50%, p=0.017) , but SVR rates were similar between those with CC and CT (88.31% vs. 75%, p=0.42). In the multivariable analysis (IL28B, age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan), EVR and RVR predicted SVR, IL28B polymorphism did not affect the SVR. RVR remains the best predictor of SVR.
Conclusion:
An IL28B polymorphism was associated with an RVR in patients infected with genotype 6. But IL28B did not predict SVR . So determination of how IL28B will be used for treatment decisions in patients with genotype 6 remains to be further studied.

20. ỦY BAN KẾT NGHĨA VIỆT - MỸ TP. SAN FRANCISCO - TP HỒ CHÍ MINH - LỄ VINH DANH CÁC CÁ NHÂN ĐÃ CÓ NHỮNG ĐÓNG GÓP QUÝ BÁU TRONG CÁC LĨNH VỰC VĂN HÓA- KHOA HỌC VÀ Y TẾ - DINH THỐNG NHẤT NGÀY 6 THÁNG 7 NĂM 2013
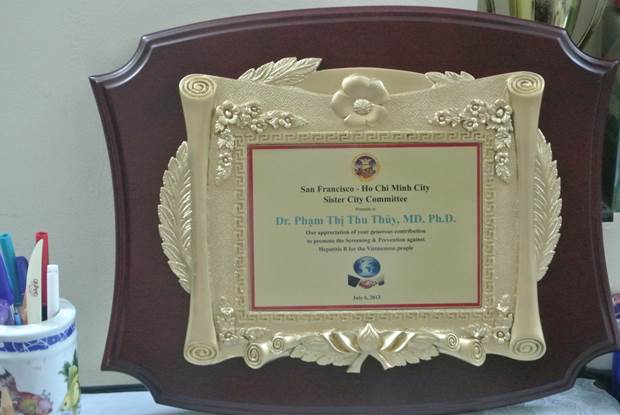





21. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TOÀN QUỐC - HÀ NỘI 28-29/09/2013
Xem nội dung báo cáo (pdf file)

22. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ - WASHINGTON DC 01--05/11/2013
POSTER 1964
Impact of Single Nuleotide Polymorphisms of IL28B rs 12979860 on SVR in Treatment Chronic Hepatitis C Genotype 6 in Vietnamese Patients.
Pham Thi Thu Thuy, Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center, HCM City
Abstract
Background:
Genetic variation in the interleukin 28B (IL28B) gene has been associated with the response to Peginterferon- alfa/ribavirin therapy in hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 1-infected patients. The importance of IL28B single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs12979860) for HCV genotype 6 infected patients is unknown.
Aims:
-To determine the relationship between IL28B single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and sustained virologic response (SVR) rates to combination therapy of Peginterferon alfa and Ribavirin.
- Comparing SNPs alle frequencies in relation to other factors such as age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan.
Method:
The study is designed as a retrospective review of the medical records of chronic HCV patients with genotype 6. SNP of IL28B (rs12979860) was identified by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of samples from 102 patients who were treated with Peginterferon alfa and Ribavirin . The duration of treatment was 48 weeks.
Results:
Patients with CC had higher rates of rapid virologic response (RVR) (84.09% vs. 50%, p=0.010), but SVR rates were similar between those with CC and CT (87.5% vs. 71.4%, p=0.20). Patients with CT had higher rates of relapse (28.57% vs. 9%), but the difference was not statistical meaningful. In the multivariable analysis (IL28B, age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan), only RVR predicted SVR, IL28B polymorphism did not affect the SVR. RVR remains the best predictor of SVR.
Conclusion:
An IL28B polymorphism was associated with an RVR in patients infected with genotype 6. But IL28B did not predict SVR. The relapse rate of patients with CT seemed to be higher than that of patients with CC. So determination of how IL28B will be used for treatment decisions in patients with genotype 6 remains to be further studied.

23. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á-THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG
Brisbane -Australia- 12-15 March 2014
The different impacts of IL28B genotype in Treatment Vietnamese Patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 and 6
Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center, HCM City
Abstract
Background:
A relationship between IL28B single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and sustained virologic response rates in combination therapy has been identified. However the impact of IL28B on SVR depends on HCV genotypes.
Aims:
We investigated the roles of polymorphism (rs 12979860) on the SVR to treatment of naive patients with HCV genotype 1 and 6.
-To determine the relationship between IL28B single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and sustained virologic response (SVR) rates to combination therapy of Peginterferon alfa and Ribavirin.
- Comparing SNPs allele frequencies in relation to other factors such as age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan.
Method:
The study is designed as a retrospective review of the medical records of chronic HCV patients with genotype 1 and 6. SNP of IL28B (rs12979860) was identified by real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of samples from 205 ( GT1=103, GT6= 102) patients who were treated with Peginterferon alfa and Ribavirin. The duration of treatment was 48 weeks.
Results:
Genotype 1 patients with CC had higher rates of rapid virologic response (RVR) (80% vs. 57.14%, p=0.036), and SVR rates were higher with CC (80% vs. 53.57%, p=0.015). Patients with CT had higher rates of relapse (33.33% vs. 16%, p=0.10), but the difference was not statistical meaningful. In the multivariable analysis (IL28B, age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan), RVR, EVR and BMI predicted SVR, IL28B polymorphism did not affect the SVR. RVR was the best predictor of SVR.
Genotype 6 patients with CC had higher rates of rapid virologic response (RVR) (84.09% vs. 50%, p=0.010), but SVR rates were similar between those with CC and CT (87.5% vs. 71.4%, p=0.20). Patients with CT had higher rates of relapse (28.57% vs. 9%, p=0.09), but the difference was not statistical meaningful. In the multivariable analysis (IL28B, age, BMI, gender, AST/ALT ratio, viral load, EVR, RVR and fibroScan), only RVR predicted SVR, IL28B polymorphism did not affect the SVR. RVR remains the best predictor of SVR.
Conclusion:
An IL28B polymorphism was associated with an RVR in patients infected with genotype 1 and 6. IL28B only predict SVR in genotype 1, not for genotype 6. The relapse rate of patients with CT seemed to be higher than that of patients with CC in both genotype 1 and 6. RVR was a strong predictor for SVR in both genotypes. Therefore IL28B should be used to predict SVR in genotype 1.

24. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT THÀNH PHỐ HỒ CHÍ MINH - 15/06/2014
Xem nội dung báo cáo (pdf file)



25. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TOÀN QUỐC - Nha Trang 26 - 27/07/2014
Xem nội dung báo cáo (pdf file)



26. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ- BOSTON- 7-11/11/2014
Poster 1462
THE DIFFERENT INCIDENCES OF HCV GENOTYPES USING TWO DIFFERENT REGIONS OF CLASSIFICATION: 5'NC AND NS5B IN VIETNAMESE PATIENTS AT MEDIC MEDICAL CENTER
Pham Thi Thu Thuy
Ho Tan Dat
Nguyen Bao Toan
Medic Medical Center- Ho Chi Minh City
ABSTRACT
Background:
HCV genotypes are clinically important for predicting the response to and determining the duration of therapy. Especially with the advent of new DAAs implying that these regimens depend on the HCV genotypes, determining genotypes is very important. Some studies indicated that using the 5'NC region to define HCV genotypes led to mis-classification of genotype 6 into genotype 1 than when using NS5B or core regions.
Aim:
- Identify HCV genotypes using 5'NC and NS5B regions.
- Identify HCV genotypes with using NS5B for the patients genotype 1 were identified by using 5'NC.
Methods:
This was a retro- sectional study. We studied 3 groups of patients: Group I included 3686 patients using 5'NC region (male 48.86%, female 51,14% with mean age of patients 49.20 ± 11.48 from January
2007 to August 2011); Group II included 176 patients using NS5B (male 43.19% , female 56.81% with mean age of patients 50.01 ± 8.63 from August 2013 to May 2014); Group III included 101 patients with genotype 1 using 5’NC who were randomly genotyped again by using NS5B (male 41.58%, female 58.42% with mean age of patients 53.12 ± 11.02 from August 2013 to April 2014).
We performed the sequencing of the hepatitis C virus genome: using 5’NC Trugene system of Siemens, using NS5B with system of ABI PRISM® 3730XL Analyzer, 96 capillary type (Applied Biosystems).
Results:
Group I: Genotype 1 was the most common 59.98% (genotype 1: 9.39%, 1a: 12.96%, 1b: 37.63%); genotype 6: 24.15% ( genotype 6: 1.28%, 6a: 22.68%, 6b: 0.19%), genotype 2: 15.82% ( genotype 2: 0.3%, 2a: 13.67%, 2b: 0.52%, 2c:1.19% and 2d: 0.14%), and genotype 3: 0.05% ( genotype 3a: 0.025% and 3b: 0.025%).
Group II: Genotype 6 was the most common: 46.59% (genotype 6: 1.14%, 6a: 19.31%, 6e: 23.86%, 6h: 1.14%, 6r: 1.14%); genotype 1: 42.05% (genotype 1a: 29.55%, 1b: 12.50%); genotype 2: 11.36% ( genotype 2a: 1.14%, 2m: 10.22%).
Group III: Genotype 1 was the most common: 78.21% (genotype 1a: 36.63%, 1b: 41.58 %); genotype 6: 19.80 % (genotype 6a: 0.99%, 6e: 14.85%, 6h: 1.98%, 6p: 0.99%, 6t: 0.99%); genotype 2: 1.98% (only genotype 2m).
Conclusion:
When using region NS5B to identify HCV genotypes, our study indicated that genotype 6 was the most common. The rate of mis-classification of genotype 6 into genotype 1 when using 5'NC was 19.80% an in this group genotype 6e had highest rate 75%.


27. Hội nghị khoa học chuyên đề nội khoa -12/07/2015 - Khách sạn Windsor Plaza
Xem nộ dung báo cáo Chẩn đoán sớm xơ gan (pdf)

28. Hội nghị Gan Mật toàn quốc - 25, 26/07/2015 - Hà Nội
Xem nội dung báo cáo Cơ hội và thách thức trong điều trị viêm gan C tại Việt Nam (pdf)


29. Lớp tập huấn: "Nâng cao năng lực cho cán bộ y tế về chẩn đoán và điều trị viêm gan virus C'
(Tháng 10-11/2015- TP Hồ Chí Minh, Cần thơ , Kiên Giang, Đà Nẵng)

30. BƯỚC ĐỘT PHÁ TRONG ĐIỀU TRỊ VIÊM GAN C 2016 - KHÁCH SẠN REX TP. HCM -24/04/2016


31. XU HƯỚNG MỚI TRONG NÂNG CAO HIỆU QUẢ QUẢN LÝ BỆNH TRUYỀN NHIỄM - Trung Tâm Hội nghị GEM - TP HCM - 19/06/2016
Xem nội dung báo cáo VAI TRÒ ĐỊNH LƯỢNG CÁC KHÁNG NGUYÊN HBV TRONG THỰC HÀNH LÂM SÀNG


32.CHẨN ĐOÁN VÀ ĐIỀU TRỊ VIÊM GAN B & C- THÁCH THỨC VÀ GIẢI PHÁP - THÀNH PHỐ HUẾ
16/07/2016
Xem nội dung báo cáo CẬP NHẬT ĐiỀU TRỊ VIÊM GAN B MẠN TÍNH (pdf file).

33. HỘI THẢO QUỐC TẾ: CÙNG HÀNH ĐỘNG VÌ MỤC TIÊU LOẠI TRỪ VIÊM GAN SIÊU VI B&C - 30-31/07/2016 -TRUNG TÂM HỘI NGHỊ TP HCM


34. VIÊM GAN SIÊU VI B&C- NHỮNG VẤN ĐỀ CẦN QUAN TÂM - KHÁCH SẠN LEGEND - TP HCM
28/08/2016


35.HỘI NGHỊ KHOA HỌC TOÀN QUỐC VỀ BỆNH TRUYỀN NHIỄM VÀ HIV/AIDS - Bệnh Viện Nhiệt Đới Trung Ương - 17 - 18/08/2016
Xem nội dung báo cáo TỐI ƯU HÓA ĐIỀU TRỊ VIÊM GAN C MẠN TÍNH VỚI CÁC THUỐC DAAs (file pdf)


36. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ- BOSTON - 11/11 - 15/11/2016
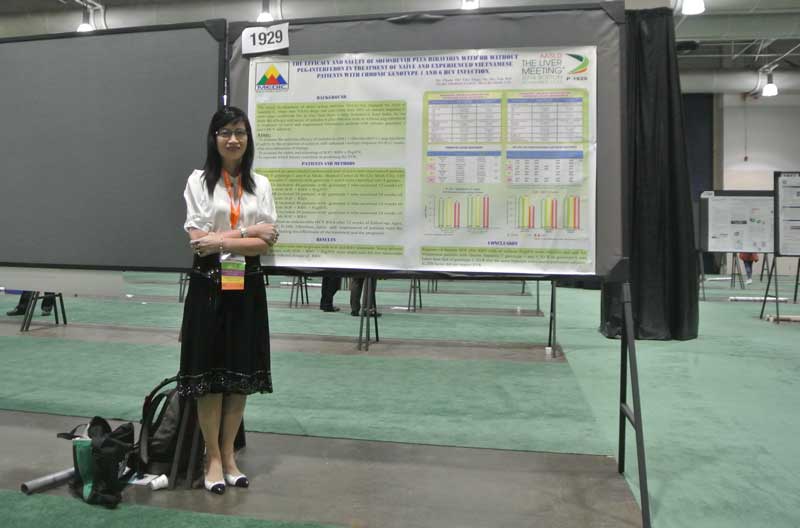
Poster 1929
THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF SOFOSBUVIR PLUS RIBAVIRIN WITH OR WITHOUT PEG-INTERFERON IN TREATMENT OF NAÏVE AND EXPERIENCED VIETNAMESE PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC GENOTYPE 1 AND 6 HCV INFECTION.
Pham Thi Thu Thu,MD,PhD
Ho Tan Dat MD
Medic Medical Center
SUMMARY:
Background.
The recent development of direct acting antivirus (DAA) has changed the field of hepatitis C. Many new DAAs drugs can cure more than 90% of chronic hepatitis C virus cases worldwide but in Viet Nam there is only Sofosbuvir from India. So we study the efficacy and safety of sofosbuvir plus ribavirin with or without peg-interferon in treatment of naïve and experienced Vietnamese patients with chronic genotype 1 and 6 HCV infection.
Aims.
- To evaluate the antiviral efficacy of sofosbuvir (SOF) + ribavirin (RBV) ± peg-interferon (PegIFN) by the proportion of subjects with sustained virologic response (SVR) 24 weeks after discontinuation of therapy.
- To evaluate the safety and tolerating of SOF+ RBV ± PegIFN.
- To consider which factors contribute to predicting the SVR.
Patients and methods.
We conducted an open-labeled randomized prospective trial of naïve and experienced patients with HCV genotype 1 and 6 at Medic Medical Center in Ho Chi Minh City. 120 chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 1 and 6 were classified into 4 groups:
-Group IA included 40 patients with genotype 1 who received 12 weeks of treatment with SOF+ RBV+ PegIFN
- Group IB included 20 patients with genotype 1 who received 24 weeks of treatment with SOF+ RBV
- Group IIA included 40 patients with genotype 6 who received 12 weeks of treatment with SOF+ RBV+ PegIFN
- Group IIB included 20 patients with genotype 6 who received 24 weeks of treatment with SOF+ RBV.
SVR was defined as undetectable HCV RNA after 24 weeks of follow-up. Ages, genders, BMI, IL28B, FibroScan, naïve and experienced of patients were the factors for evaluating the effectiness of the treatment and the prognosis.
Results.
SVR of group IA was 100%, IB was 90%, IIA was 100%, IIB was 100%. (p>0.05)
Two patients of group IB relapsed: one naïve , genotype 1b, FibroScan F4 and another experienced, genotype 1b, FibroScan F4.
The adverse events were rare in groups with SOF and RBV treatment. Some adverse events in groups with SOF+RBV +PegIFN were slight and did not necessitate medication or reduced dosage of RBV.
Conclusion.
Regimes of therapy SOF plus RBV with or without PegIFN were effective and safe for Vietnamese patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 and 6. SVR in genotype 6 was better than that of genotype 1. SVR was the same between naïve and experienced subjects. IL28B factor did not impact SVR.
37. Hội thảo vệ tinh: KỶ NGUYÊN MỚI TRONG QUẢN LÝ BỆNH VIÊM GAN VIRUS C MẠN - KHÁCH SẠN NEW WORLD - TP. Hồ Chí Minh - 17/12/2016
Xem nội dung báo cáo HIỆN TRẠNG VÀ THÁCH THỨC TRONG CHẨN ĐOÁN & ĐIỀU TRỊ HCV MẠN TÍNH TẠI VIỆT NAM


38. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT CHÂU Á- THÁI BÌNH DƯƠNG - Thượng Hải- Trung Quốc, 15 - 18/2/2017
1. Poster PP 0214
Impact Of a 12-Week Oral Regimen of Elbasvir/Grazoprevir (EBR/GZR) On Health-related Quality of Life (HRQOL) and Fatigue In Treatment-Naïve Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Genotype (GT) 1, 4, or 6 Infection: Data from the C-CORAL Study
2.Presentation
Sofosbuvir + Ribavirin for 24 weeks or Sofosbuvir + Pegylated-interferon + Ribavirin for 12 Weeks in Genotype 1 or Genotype 6 HCV-infected Patients: Results from a Phase 3 Study in Vietnam
39. HỘI THẢO QUỐC TẾ: CÙNG HÀNH ĐỘNG VÌ MỤC TIÊU LOẠI TRỪ VIÊM GAN B& C TẠI VIỆT NAM - Trung Tâm hội nghị TP HCM - 29-30/07/2017
Viêm gan C và rượu (Nội dung tham luận - pdf file)

40. HỘI NGHỊ TRUYỀN NHIỄM TOÀN QUỐC - Ninh Bình 08 - 09/09/2017
TAF - Lựa chọn mới -Hiệu quả -An toàn trên thận & xương cho bệnh nhân viêm gan siêu vi B mạn.
TS.BS.Phạm Thị Thu Thủy
Trung Tâm Y Khoa Medic-TP HCM
Theo WHO năm 2017 ước tính 257 triệu ngưới đang sống với bệnh viêm gan do HBV. Trong đó tỷ lệ hiện mắc viêm gan do HBV trên người trưởng thành mắc bệnh ở Tây Thái Bình Dương là cao nhất 6,2%, theo sau đó là tỉ lệ xơ gan và ung thư gan ngày càng tăng.
Vấn đề điều trị còn nhiều khó khăn và phức tạp. Thuốc tiêm Peg IFN thì đắt tiền và nhiều tác dụng phụ, các loại thuốc uống thì uống rất lâu dài, gần như không hạn định thời gian...Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) được đánh giá là có hiệu quả cao, tuy nhiên ảnh hưởng nhiều đến xương và thận. Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF) là loại Tenofovir mới với các ưu điểm: sự ổn định trong huyết tương tốt hơn TDF, tăng phân phối thuốc hoạt động đến tế bào gan, giảm lượng TFV trong tuần hoàn do đó có thể giảm liều TAF còn 25mg. Dùng không ảnh hưởng xương và an toàn cho thận.
Nghiên cứu của Maria và cs (Lancet 2016) trên 426 bệnh nhân HbeAg âm tính cho thấy TAF hiệu quả như TDF nhưng an toàn cho xương và thận. Nghiên cứu của Henry Chan và cs (Lancet 2016) trên 1473 bệnh nhân HBeAg (+) cũng cho kết quả tương tự. Nghiên cứu của M. Brunetto và cs (EASL 2017) trên 425 bệnh nhân HBeAg âm tính được điều trị ngẫu nhiên TAF 25mg hay TDF 300mg, ở tuần 96 , đáp ứng virus của TAF là 90% và của TDF là 91%. Tỉ lệ bình thường men ALT của nhóm TAF cao hơn TDF (81% vs. 71%, p=0,038)
TAF hiện nay là thuốc uống được chọn lựa đầu tay cho điều trị viêm gan B vì khả năng ức chế virus cao , không kháng thuốc, an toàn cho xương và thận, đặc biệt dùng an toàn cho người lớn tuổi , người có tiền sử bệnh xương và người có chức năng thận yếu.
TAF- New – Effective - Safe Option for kidney & bone in patients with chronic hepatitis B.
Pham Thi Thu Thuy, M.D., Ph.D.
Medic Medical Center - HCMC
According to WHO’s estimation, the number of people with hepatitis caused by HBV is about 257 million in 2017. Among these, adults ratio with hepatitis caused by HBV in the Western Pacific is 6.2%, which is the highest percentage, and is followed by an increasing ratio of cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Treatments have faced numerous difficulties and complexities. Peg IFN injections are expensive and have many side effects; some other oral medicines require a long treatment time, and some with uncertain duration. Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) is considered to be highly effective. However it has damaging side effects on the bones and kidneys. Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF) is a new type of Tenofovir with advantages such as greater plasma stability in comparison with TDF, enhancement delivery of active drug to hepatocytes, and TFV reduction in the circulation which can lead to the reduction of TAF to 25 mg. Using this has no side effects on bones and is safe for kidneys.
A study by Maria et al. (Lancet 2016) on 426 HBeAg-negative patients showed that TAF was as effective as TDF and is safe for bones and kidneys. The study by Henry Chan et al. (Lancet 2016) on 1473 patients with HBeAg- positive also showed similar results. In the study of M.Brunetto et al . (EASL 2017) , 425 patients with HBeAg- negative were randomized to receive TAF 25mg or TDF 300 mg. At week 96 , virologic response rates were 90% and 91% in the TAF and TDF groups respectively. A greater percentage of TAF patients achieved normalization of serum ALT values (81% vs. 71%, p=0,038).
TAF is currently the first choice of oral drug for the treatment of hepatitis B because of its high rates of virological suppression, no evidence of virological resistance, better renal and bone safety profile than TDF. Especially for older people and people with a history of bone diseases and weak renal function.

41. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TOÀN QUỐC - HUẾ 4 - 5/11/2017
VIÊM GAN SIÊU VI C VÀ RƯỢU BIA
TRƯỜNG HỢP LÂM SÀNG
TS.BS. Phạm Thị Thu Thủy
BS. Hồ Tấn Đạt
Trung Tâm Y Khoa Medic- TP HCM

42. Bài đăng tạp chí Journal of clinical virology
Background: To avoid false negative results, hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) assays need to detect samples
with mutations in the immunodominant ‘a’ determinant region, which vary by ethnographic region.
Objective: We evaluated the prevalence and type of HBsAg mutations in a hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected Eastand
Southeast Asian population, and the diagnostic performance of the Elecsys® HBsAg II Qualitative assay.
Study design: We analyzed 898 samples from patients with HBV infection from four sites (China [Beijing and
Guangzhou], Korea and Vietnam). HBsAg mutations were detected and sequenced using highly sensitive ultradeep
sequencing and compared between the first (amino acids 124–137) and second (amino acids 139–147)
loops of the ‘a’ determinant region using the Elecsys® HBsAg II Qualitative assay.
Results: Overall, 237 distinct amino acid mutations in the major hydrophilic region were identified; mutations
were present in 660 of 898 HBV-infected patient samples (73.5%). Within the pool of 237 distinct mutations, the
majority of the amino acid mutations were found in HBV genotype C (64.8%). We identified 25 previously
unknown distinct mutations, mostly prevalent in genotype C-infected Korean patients (n=18) followed by
Chinese (n=12) patients. All 898 samples were correctly identified by the Elecsys® HBsAg II Qualitative assay.
Conclusions: We observed 237 distinct (including 25 novel) mutations, demonstrating the complexity of HBsAg
variants in HBV-infected East- and Southeast Asian patients. The Elecsys® HBsAg II Qualitative assay can reliably
detect HBV-positive samples and is suitable for routine diagnostic use in East and Southeast Asia.
43. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ-2018 - San Francisco 09/11 - 13/11/2018
Abstract 1634 – HEPATOLOGY- Vol 68, October 2018, Supplement 1
HIGH PREVALENCE OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS INFECTION IN THE RURAL AREAS OF THE MEKONG DELTA PROVINCES, VIETNAM
Pham Thi Thu Thuy, Assoc.Prof, PhD, MD
Ho Tan Dat MD
Nguyen Bao Toan MD
Medic Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
1. Background and Aims: Previous studies have claimed the HCV infection rate in Vietnam is at about 1-4% of the population; this rate is considerably higher in the high-risk subjects such as intravenous drug users, commercial sex workers, and dialysis patients… However, data of HCV infection rates of rural areas of Vietnam is limited. Therefore, we conduct the research in Kien Giang province - a rural area of Mekong Delta, with two purposes:
2. Methods: We randomly selected participants by their residential group to conduct an Anti HCV screening test. If the result was positive, HCV quantification and genotyping were evaluated. We then analyzed the correlation between HCV infection rate with age and gender, the correlation between genotype and viral load, and the correlation between gender and genotype. 3,763 people were selected for the Anti HCV test.
3. Results: 334 people were positive, accounted for 8.87%, in which male infection rate was higher than female, 10.9% and 7.3% respectively (p=0.0016). Age group under 20 years old accounted for 5.88%, 20-40 accounted for 5.31%, and 40-60 accounted for 8.82%, older than 60 had the highest infection rate at 15.93% (p = 0.0001). Of the 334 people with Anti-HCV positivity, there were 242 people with HCV RNA positivity, accounted for 72.45%. Genotype 1 was at 46.6% (1a: 32.2%, 1b: 14%), Genotype 2 was at 7.9 % (2a: 2.5%, 2m: 5.4%), Genotype 6 was at 45.5% (6a: 10.3%, 6e: 21.5%, 6h: 11,2%, 6k: 0.4%, 6l: 1.2%, 6o: 0.8%). With genotype 1 and 6, most of the viral loads were below 800,000 IU/mL. With genotype 2, the percentage of those with a viral load above 800,000 IU/mL was similar to those below. With genotype 1 and 2, male and female infection rates were similar. With genotype 6, male infection rate was higher than female, at 59.1% and 40.9% respectively (p = 0.01).
4. Conclusion: HCV infection rate in rural Kien Giang was at 8.87% with more males than females acquired HCV. Infection rate in older than 60 year old group was very high, at 15.93%. Over all, genotype 1 was at 46.6%, genotype 2 was at 7.9%, and genotype 6 was at 45.5%. The viral load was low except for genotype 2. In genotype 6, there were more males than females.

44. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TP HỒ CHÍ MINH - KS Equatorial TP. HCM - 16/12/2018
Điều trị viêm gan siêu vi C ở bệnh nhân bệnh thận mạn trong thực tế lâm sàng Việt Nam

45. Singapore Hepatology Conference 7-8 June 2019
M2BPGi as a novel liver fibrosis staging biomarker for chronic hepatitis B and C

46.HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ 2019 - Boston 08-12/11/2019
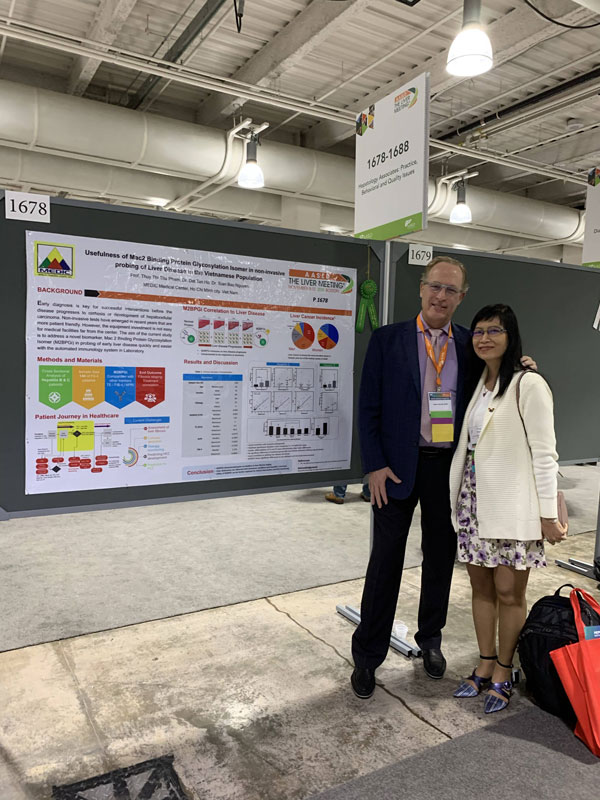
Abstract 1678 – HEPATOLOGY- Vol 70, October 2019, Supplement 1
Usefulness of Mac2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer in non-invasive probing of Liver Disease in the Vietnamese Population
Assco.Prof.Pham Thi Thu Thu Thuy,
MD,PhD
Ho Tan Dat,
MD
Nguyen Bao Toan,
MD
Medic Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
Background
Early diagnosis is key for successful interventions before the disease progresses to cirrhosis or development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Non-invasive tests have emerged in recent years that are more patient friendly. However, the equipment investment is not easy for medical facilities far from the center. The aim of the current study is to address a novel biomarker in probing of early liver disease quickly and easier with the automated immunology system in Laboratory.
Methods and Materials
This is a cross sectional study involving randomly selected patients seeking treatment in Medic Medical Center, Viet Nam from January to April 2019. Patients were selected from diverse liver disease etiologies. Intuitional review board (IRB) is waived as residual blood samples from routine clinical tests are utilized. The study addresses the clinical comparisons of mac2 binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) with different clinical parameters, co-morbidities and transient elastography (TE) results. M2BPGi is measured from blood samples using a sandwich immunoassay. A total of 140 patient samples were analyzed.
Results
Our results indicated good correlations to TE for liver fibrosis staging using M2BPGi. The patient cohort was divided based on etiology and one-way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) showed significant differences between F0-1; F2; and > F3 patient groups. Further analysis of F3 and F4 stages for Hepatitis C patients showed the cirrhotic group had two-fold higher M2BPGi levels and was statistically significant using a Student t test. In comparisons with APRI and FIB-4, a significant correlation was observed with M2BPGi. Addressing the different etiologies critical in our patient group with early disease (F0-1), we observed M2BPGi to be dominated by viral hepatitis effects. No statistical significant results were observed between HCV and HCV/NAFLD cohorts. This holds similar true for HBV and HBV/NAFLD patients. M2BPGi was observed to be etiology specific with Hepatitis C patients with early liver disease having higher M2BPGi levels than Hepatitis B patients. For viral load correlations critical for disease monitoring especially for hepatitis B, we observed strong positive correlation with M2BPGi levels. Mean M2BPGi levels for hepatitis B patients with viral load lower than 2000 IU/mL were 1.75-fold lower than those with greater than 2000 IU/ mL.
Conclusion
M2BPGi was observed to be a good indicator for early disease in patients with different etiologies. Our work is the first to address mixed etiology testing of this marker and demonstrated significant correlations with existing routine assays and treatment monitoring. The results provide reference cutoffs in different causes of liver disease and validates the utility for early disease monitoring. This is useful for the far regions of developing countries.
AWARD: DISTINCTION POSTER

47. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TOÀN QUỐC - 29 - 30/11/2019 KS. ADORA - TP. HCM
GIÁ TRỊ CÁC CHỈ DẤU UNG THƯ TRONG HCC (pdf file)



48. Bài đăng trên Tạp chí Y khoa thế giới
1. World journal of hepatology
2. Journal of infectiuos disaese and pathology

49. HỘI NGHỊ: Cập nhật điều trị viêm gan virus B mạn - Ngày 24/10/2020 – TP Hồ Chí Minh
TAF - Lựa chọn mới cho điều trị viêm gan siêu vi B mạn (pdf)

50. HÔI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TOÀN QUỐC - 25/10/2020 - REX HOTEL - TP HCM

51. HỘI NGHỊ: ỨNG DỤNG Y HỌC THỰC CHỨNG VÀO THỰC HÀNH LÂM SÀNG
Hội Y học TP Hồ Chí Minh tổ chức ngày 08/11/2020 tại Trung Tâm Hôi nghị TP HCM
Xét nghiệm viêm gan siêu vi: Chỉ định và biện luận kết quả(pdf)

52. HÔI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ - 13/11 - 16/11/2020 - Hội nghị online.
Poster 1138:
Values of AFP, AFP-L3, PIVKA II markers in early detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis patients
Pham Thi Thu Thuy- Phung Huy Hoang- Ho Tan Dat
Medic Medical Center- Ho Chi Minh City
115 People Hospital – Ho Chi Minh City
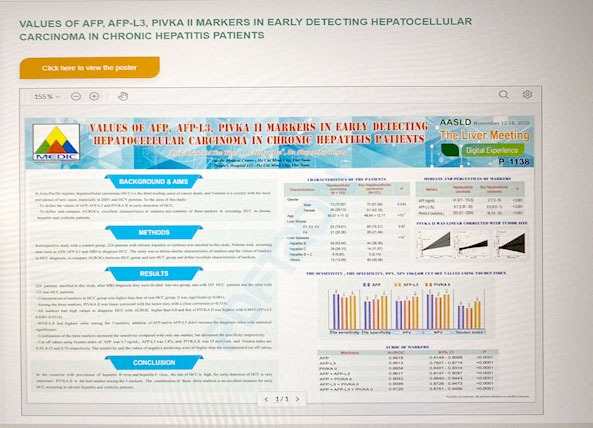
I. Aims:
In Asia-Pacific regions, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third leading cause of cancer death, and Vietnam is a country with the most prevalence of new cases, especially in HBV and HCV patients. So the aims of this study:
-To define the values of AFP, AFP-L3 and PIVKA II in early detection of HCC
-To define and compare AUROCs, excellent characteristics of markers and combine of three markers in screening HCC in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis patients.
II. Methods:
Retrospective study with a control group. 224 patients with chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis was enrolled in this study. Patients took screening tests such as AFP, AFP-L3 and MRI to diagnose HCC. The study was to define similar characteristics of markers and the values of markers in HCC diagnosis, to compare AUROCs between HCC group and non HCC group and define excellent characteristics of markers.
III. Results:
224 patients enrolled in this study, after MRI diagnosis they were divided into two group, one with 103 HCC patients and the other with 121 non HCC patients.
-Concentration of markers in HCC group was higher than that of non HCC group. It was significant (p<0.001).
-Among the three markers, PIVKA II was linear corrected with the tumor size, with a close correction (r=0.553).
-All markers had high values to diagnose HCC with AUROC higher than 0.8 and that of PIVKA II was highest with 0.8855 (95% CI: 0.8401-0.9314).
-PIVKA II had highest value among the 3 markers, addition of AFP and/or AFP-L3 didn’t increase the diagnosis value with statistical significance.
-Combination of the three markers increased the sensitivity compared with only one marker, but decreased the specificity respectively.
-Cut off values using Youden index of AFP was 4.7 ng/mL, AFP-L3 was 1.8%, and PIVKA II was 35 mAU/mL and Youden index are 0.59, 0.53 and 0.70 respectively. The sensitivity and the values of negative predicting were all higher than the recommended cut off values.
IV. Conclusion:
In the countries with prevalence of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus, the rate of HCC is high. So, early detection of HCC is very important. PIVKA II is the best marker among the 3 markers. The combination of these three markers is an excellent measure for early HCC screening in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis patients.53. CHƯƠNG TRÌNH HÔI THẢO KỸ NĂNG VIẾT BÀI BÁO KHOA HỌC - ACADEMIC WRITING COURSE - HỘI Y HỌC TP HCM- ONLINE
How to submit a paper and get it published - Sharing Experience from Vietnam (.pdf file)

54. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TP HỒ CHÍ MINH- ONLINE - 21/11/2021


55. Bài đăng trên tạp chí y khoa quốc tế BIR BRITISH JOURNAL OF RADIOLOGY
Infantile mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver with elevated alpha fetoprotein(.pdf file)

56. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT TP HỒ CHÍ MINH - KS.Equatorial, 24/07/2022
Nội dung báo cáo: Viêm gan Virus B và thai kỳ - Dữ liệu mới từ TAF (.pdf file)


57. Hội nghị ngày Viêm gan thế giới - Hà Nội 28/07/2022
Quan điểm mới về viêm gan Virus từ AASLD 2021- DDW 2022 - EASL 2022 (.pdf file)


58. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ - WASHINGTON DC, 4/11 - 8/11/2022
POSTER 4401: Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) Methylation Profile Improves the Accuracy of Serum Biomarkers (AFP, AFP-L3, and DCP) for the Detection of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Background
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer death, with rates highest in transitioning countries. Late detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) limits its overall 5-year survival rate to < 16%. Current diagnostic tests based on serum protein biomarkers give high false-positive results, and despite improvements, early cancer detection continues to face challenges. Increasing evidence indicates that early carcinogenic hallmarks, such as aberrant DNA methylation, involved in dysregulation of tumor-associated genes, represent potential blood based markers for the early detection of HCC.
Methods and Materials
Using a panel of 450 target regions consisting of 18,000 CpG sites, we examined differences in circulating methylated DNA profiles between 51 patients with early stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and 86 healthy individuals to identify multiple differentially methylated regions (DMRs). The identified DMRs were exploited to build machine learning classifiers to discriminate plasma samples from early-stage HCC patients and healthy subjects. We further validated the performance of our methylation based models either alone or in combination with the μTASWako markers in an independent at-risk cohort consisting of 46 patients with HCC and 49 patients with chronic liver hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Results
Our findings showed that circulating plasma DNA shed by tumors from early-stage HCC patients was hypermethylated at multiple regulatory regions and enriched in HCC cancer-associated genes. Our random forest models built from those DMRs achieved an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.8 (95%CI: 0.79-0.8) in differentiating 46 early-stage HCC patients from 27 cirrhosis, and 22 hepatitis patients, outperforming individual serum biomarkers (AFP, AFP-L3, and DCP) used in a commercial diagnostic test, μTASWako. Interestingly, combining our model with the three μTASWako biomarkers provided additive diagnostic power, with an AUC of 0.86, sensitivity of 70.4% (95%CI: 68.8%-71.9%), and specificity of 91.4% (95% CI: 89.9%-93.0%).
Conclusions
Our studies demonstrated that HCC-specific methylation signatures in circulating plasma DNA could serve as biomarkers for improving the accuracy of current assays in differentiating early-stage HCC patients from at-risk individuals. Further clinical evaluation of our assay performance in a large-scale prospective study is warranted.
59. Hội nghị Khoa học Kỷ niệm 100 năm Ngày sinh Cố Thủ Tướng Võ Văn Kiệt - 20/11/2022 - Vĩnh Long
Cập nhật điều trị Gan nhiễm mỡ không do rượu(.pdf file)




60. Hội nghị Khoa học Hội Y Học TP HCM - 03/12/2022
Chủ để: Thai phụ và các vấn đề liên quan
Bài tham luận: Viêm gan virus B và thai kỳ(.pdf file)




61. HỘI NGHỊ KHOA HỌC QUỐC TẾ - 11-12/06/2023 - ĐẠI GIẢNG ĐƯỜNG – ĐẠI HỌC Y DƯỢC TP HCM
Hội nghị được tổ chức bởi sự phối hợp Đại học Johns Hopkins ( USA) – Hội Y Học TP HCM- LCH Gan Mật TP HCM- LCH Ung thư TP HCM
Chủ đề:
Bài tham luận: Ung thư gan ở người trẻ nhiễm virus viêm gan B mạn: Những thử thách và giải pháp (.pdf file)



62. HỘI THẢO KHOA HỌC - Ngày 12/08/2023 - KS Intercontinental – TP HCM
Do Công ty Roche phối hợp Bệnh viện Ung Bướu TP HCM tổ chức với chủ đề:
Bài tham luận:
Các dấu ấn hiện tại và mới liên quan ung thư biểu mô tế bào gan- hcc. ứng dụng lâm sàng(.pdf file)



63. HỘI NGHỊ KHOA HỌC: Ngày 08/10/2023 - KS Equatorial – TP HCM
Do LCH Gan Mật TP HCM tổ chức với chủ đề: Những vấn đề thời sự hiện nay về bệnh gan mật năm 2023
Bài tham luận:Giá trị của HBcrAg trong chẩn đoán và Tiên lượng viêm gan virus B (.pdf file)


64. HỘI NGHỊ GAN MẬT HOA KỲ - BOSTON, 10/11 - 14/11/2023
POSTER 1312-C: Exploring Mac2-binding Protein glycosylation isomer diagnostic potential for non-invasive testing of Liver Disease in Vietnamese HBV Patients - Prpf. ThuThuy Pham Thi, Dr Dat Tan Ho, Toan Bao Nguyen


Background
The study aims to explore the value driven care approach of utilizing serum based Mac2-binding Protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) as a novel biomarker for the early detection of liver fibrosis and monitoring of anti-viral treatment response in patients with chronic hepatitis B (HBV). Non-invasive testing is patient friendly, and this work aims to fill critical gaps to derive clinical decision cut-offs for liver fibrosis staging and track responses of patients during treatment.
Methods and Materials
This is a cross sectional study involving 334 mono-infected chronic HBV patients. The study receives ethical approval from Medic Medical Center, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Treatment naïve patients were recruited with baseline M2BPGi taken, and additional serial measurements at 3 and 6-month intervals. M2BPGi is measured via an automated chemiluminescence immunoassay (Sysmex, Japan) using residual serum samples. Kruskal-Wallis tests were used to ascertain the statistical significance of M2BPGi for fibrosis staging and variations at different serial measurements. Area under the receiver operating characteristics (AUROC) curve was computed comparing M2BPGi levels with different biomarkers. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Baseline M2BPGi median levels provided specific cut-offs relevant for liver fibrosis staging in comparison with classical biomarkers and transient elastography (TE). Baseline levels were found to be highly correlative to TE results (Pearson, ρ = 0.71, p-value <0.0001). Median M2BPGi levels were 0.73, 0.92, 1.57 and 3.19 cut-off index (C.O.I.) across F0-1, F2, F3 and F4 cases respectively. To ascertain the diagnostic potential, AUROC was computed among these cases addresses early disease and cirrhosis. Between F2 and F3 cases, AUROC was 0.79, which presents strong performance measurements to discriminate early liver disease cases. Furthermore, AUROC between cirrhotic cases and F3 was 0.88, suggesting M2BPGi can be clinically useful in distinguishing advanced liver disease. Serial M2BPGi measurements showed monotonic decreasing trends among the patient cohorts across different fibrosis stages. Median levels reduced by 35% at 6-month for M2BPGi and 10% using TE. Interestingly, TE at 3-month were non-significant for the treated patients but observed a reduction of 25% using M2BPGi.
Conclusion
Within the current HBV cases, M2BPGi displayed excellent discriminatory levels among different fibrosis stages prior to treatment. This work is the first in Vietnam that extensively validated the marker with specific decision limits. As a non-invasive test, M2BPGi can be easily integrated into existing testing programs for concurrent profiling of liver disease in chronic HBV. Early diagnosis of fibrosis adds value to reduce healthcare burden and prevents disease progression. In comparison with TE, we observed a better dynamic range using M2BPGi when tracking treated cases.
65. HỘI NGHỊ KHOA HỌC THƯỜNG NIÊN NĂM 2023 NGÀY 09/12/2023 TẠI TRUNG TÂM HỘI NGHỊ 272 VÕ THỊ SÁU -Q3- TP HCM
Hội Y Học tổ chức với chủ đề: Cập nhật chẩn đoán và điều trị các bệnh thường gặp tại Phòng khám và Tuyến Y tế cơ sở.
Bài tham luận: Tầm soát viêm gan siêu vi B : Cần làm gì sau khi có kết quả HBsAg dương tính(.pdf file)


